#Research & Development
STFI is investigating textile applications for PU casting compounds
Casting compound meets textile
The Sächsische Textilforschungsinstitut e.V. (STFI) is currently developing two applications on textiles. On the one hand, the PU casting resins are being investigated as a cover layer for sensors that are used to monitor mechanical load . The second approach is dedicated to 3D printing on pre-tensioned textiles in order to subsequently create three-dimensionally shaped structures.
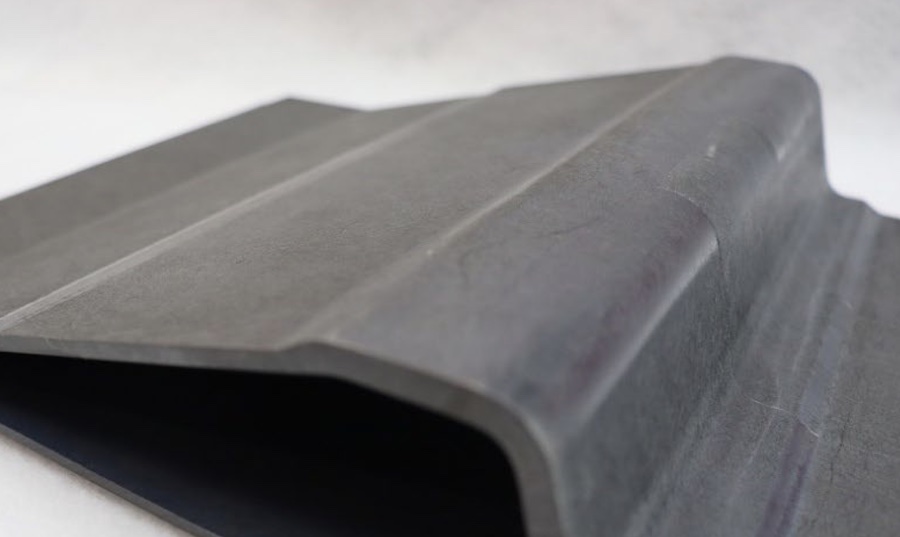
The current research project “Texsafe” (Reg. No. 49MF220096) focuses on the development of large-area textile sandwich-structured surface elements for monitoring mechanical loads . Suitable coating materials should permanently measure the permittivity in order to detect changing mechanical parameters by elastic deformation. In addition, these materials must withstand large loads of up to 1000 kg without being destroyed and protect the textile from mechanical damage. In the course of the investigations, polyurethane-based casting resins from WEVO-CHEMIE GmbH, Ostfildern-Kemnat, have proven to be particularly suitable because they have tough elastic properties and a high elongation at break. The products of the Wevopur series meet these requirements and have already been successfully tested in extensive test series successfully. The first small-scale functional models were produced as part of the project, which enable the detection of mechanical loads (Figure 1). The potting compound proved to be particularly suitable for this application due to its low mixed viscosity, as the textile was well wetted or saturated . In a next step, the scaling to large-area textile sandwich-structured surface elements is to take place. The textiles finished in this way can be used in particular in truck loading space area recognition, for parking lot and floor sensor technology for access control and monitoring areas.

3D printing on textiles has been the subject of successful developments of the STFI. In this context, new materials for the different 3D application processes are tested. Within the framework of the research project “Machine and process development for 3D printing on pre-stretched textiles” (Reg. No. KK5081706WO1), selected Wevopur products were also .
The application for this special 3D printing requires printing materials that have high flexural strengths and SHORE hardnesses in the upper Shore D range, in order to reinforce pre-stressed textiles using 3D printing . In the experiment, stretchable PES knitted fabrics were tensioned homogeneously and without distortion in the longitudinal and transverse directions using a newly developed tensioning system with defined forces. Subsequently, the textiles were printed with various geometries using 3D printing. In addition to the classic FDM process, which uses thermoplastic filaments, the LDM process was also tested. In this process, pasty materials or liquids are processed.
Here, too, products from the Wevopur series proved to be desirable. The materials were applied to the pre-stretched textiles using a 2-component print head, thus reinforcing them at specific points. After the printed textile was released, defined deformations occurred defined deformations. This is also referred to as 4D printing. This technology can be used, for example, to manufacture individual textile lampshades or acoustic panels (Figure 2) and opens up further application possibilities in architecture . In the project, a good and durable bond with the textile was ensured, which is due to the customized viscosity and good adhesion of the Wevo materials (such as WEVOPUR 71/25 MT/3 with WEVONAT 30 0).

The successful tests of polyurethane-based potting compounds in combination with textiles at STFI show new application potentials for the Wevopur product series from WEVO-CHEMIE GmbH.
Further information: http://www.stfi.de