#Research & Development
The VR glove from the 3D printer
Research sometimes needs a sacrifice. Empa researcher Patrick Danner has just made one – and filmed it. "When I applied a good 2000 volts to the sample, it caught fire," he reports drily in the debriefing. The mishap is clearly visible in his cell phone video: First it smokes, then flames erupt from the experimentally created polymer. "Hopefully, you were still able to save a piece of it," counters Dorina Opris, head of the "Functional Polymeric Materials" research group. A piece of evidence is important to learn from the result and draw conclusions.

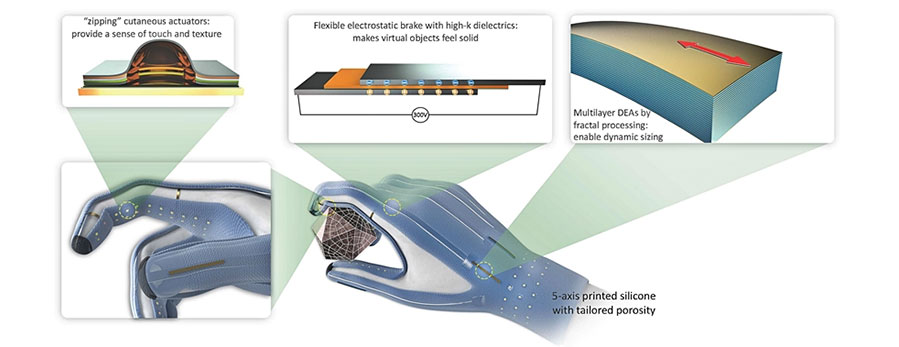
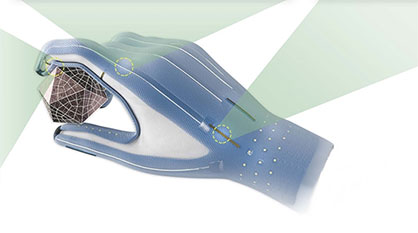
With their research on electroactive polymers, Dorina Opris and Patrick Danner are part of a large-scale project called "Manufhaptics". The goal of the four-year project, led by Herbert Shea of the Soft Transducers Lab at EPFL, is a glove that makes virtual worlds tangible. Crucially, all of the glove's components, which exert various forces on the surface of the hand, are to be producible in a 3D printer. So this is about research into new materials, with the production method being considered from the very start.
Three types of actuators
To make virtual surfaces feel real and objects tangible at the right size, the research teams from EPFL, ETH Zurich and Empa want to integrate three different types of actuators into the glove: Underneath the fingers, nubs can grow up to replicate a specific texture of a surface. In the area of the finger joints, electrostatic brakes are mounted that stiffen the glove and block the joints. This simulates larger, solid objects that offer resistance when touched. The third type of actuators that complete the virtual experience are called DEA's (Dielectric Elastomer Actuator). These DEA's are used on the back of the hand; they tighten the outer skin of the glove so that it fits perfectly at all points. During the VR experience, they can also apply pressure to the surface of the hand. The DEA's are Empa's topic.
Dorina Opris, the head of the research group, has years of experience with such electroactive polymers. "They react to electric fields and contract like a muscle," the researcher explains. "But they can also serve as a sensor, absorbing an external force and generating an electrical pulse from it. We're also thinking of using them to harvest energy locally: From movement, electricity can thus be generated anywhere."
The Manufhaptics project presents new challenges for Opris and her colleague Patrick Danner. "Until now, we have produced our polymers using solvents through a chemical synthesis," explains Opris. Now everything has to work without solvents: The plan is to superimpose up to 1000 fine layers from the 3D printer, always alternating between the electroactive polymer and a current-conducting layer. "Solvent has to be avoided in such a process" says Opris. Patrick Danner explains the next difficulty: The two inks needed for making the layers must have the exact right consistency to flow out of the 3D printer's nozzle. "Our project partner Jan Vermant from ETH Zurich wants something with similar properties to a hand cream. It should come out of the printer easily and then remain dimensionally stable on the base." And after that, this "creamy" layered structure still needs to crosslink into the appropriate polymer.
After a long series of tests, Patrick Danner found a promising formulation – a cream that is liquid enough and at the same time dimensionally stable, and from which electroactive polymers can be created in a single step. His colleague Tazio Pleji at ETH Zurich, a member of Jan Vermont's team, has successfully processed the material in his 3D printer into several layers – always alternating between polymer and electrode material. There are not yet 1,000 layers, but only about 10, and the artificial muscle from the 3D printer does not yet function satisfactorily.
The competition is at Harvard
But Opris and Danner are confident of mastering the task together with the printing specialists at ETH Zurich – possibly as the first team in the world. The only scientific competitors in this field are based at the renowned Harvard University in Massachusetts. "I know the colleagues there from some congresses," says Dorina Opris. "We watch very closely what they are upt to. And they're certainly watching our work, too."

















