#Research & Development
Detect errors early and save costs
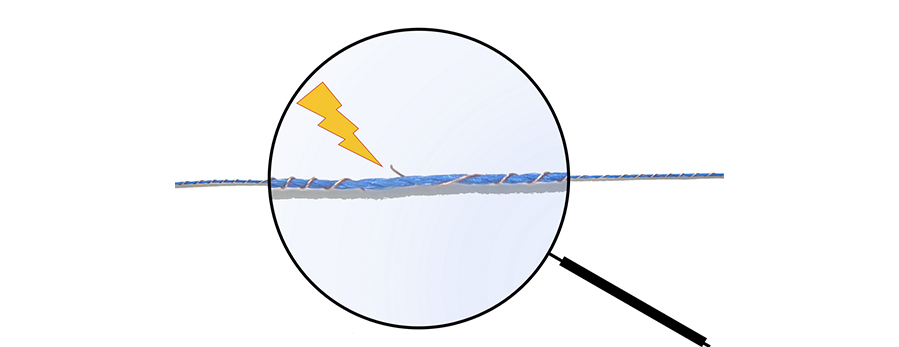
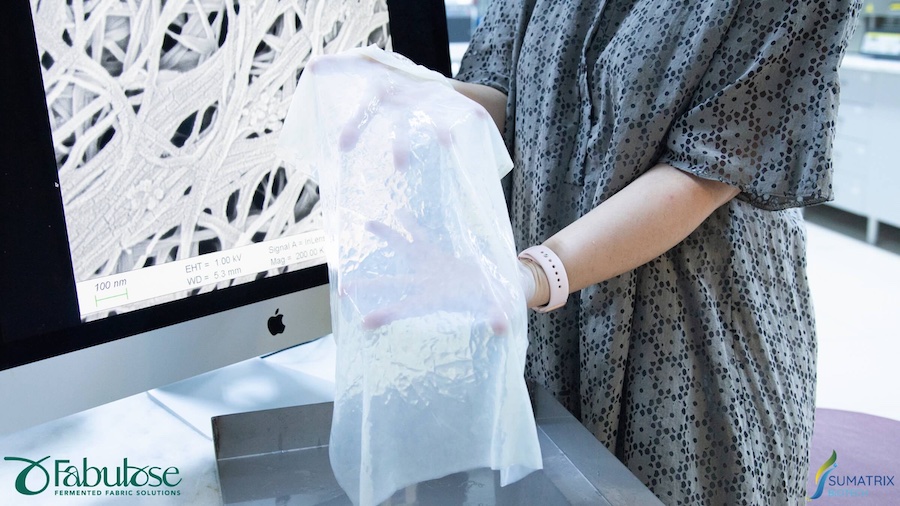
For highly elastic smart textile products, yarns often are used that consist of both conductive and non-conductive components. For this purpose conventional highly elastic yarns can be wound with conductive fine wires. The elasticity of the yarn component is largely retained in this way. During knitting, however, the yarns are subjected to such high stresses that the conductive yarn components can be damaged. Since this often does not break the entire yarn, the defect is not detected during the knitting process in current production procedures. In extreme cases, the finished knitted part is a reject. In the case of fully-fashioned knitted parts, the financial damage is particularly great because of the relatively low productivity of the flat knitting process and the relatively high loss of production time.
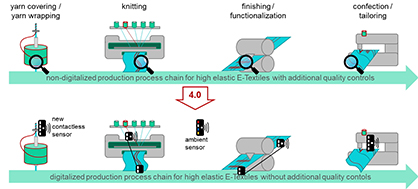
In order to detect faults in electrical properties already during the manufacturing process, the SensorStrick 4.0 research project is recording process and environmental data during textile production at various process stages.
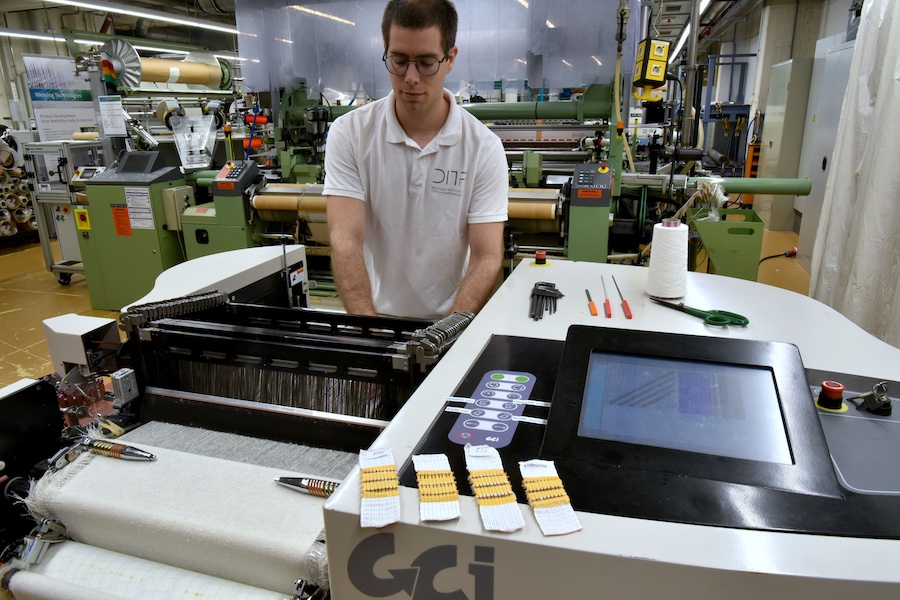
For this purpose, wrapping and flat knitting machines are equipped with distributed sensor technology that measures temperature, humidity, light, proximity and yarn tension as well as yarn speed. In addition, microphones monitor noise in the immediate production environment. These acoustic measurement data indicate vibrations, for example, and can be evaluated particularly well by using artificial intelligence. In wrapping yarn production, the recorded process variables are used directly to control the process parameters.
In addition, new low-cost sensors are being developed. For running yarns, for example, a principle has been developed with four measuring tubes that measure quickly and without contact how conductive the yarn passing through is and what its sensory properties are. These sensors are designed in such a way that they can be used in as many textile processes as possible without having to adapt them to different processes at great expense.
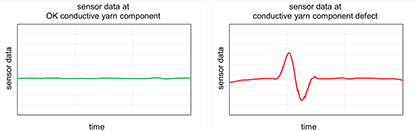
The yarns are thus monitored both during wrapping yarn production and in the subsequent knitting process. If a break occurs in the conductive yarn component, it is detected immediately. Humidity and ambient temperature do not affect the measuring accuracy. Process monitoring works not only for knitted fabrics, but also for other textile surfaces.
In the further course of the project, the sensors will be used in the production of highly elastic wrapping yarns and knitted parts and will be tested to see how effectively any faults that occur are detected.
With these newly developed methods, defective semi-finished products can be removed from the process chain in good time. Expensive additional inspections during later process steps become superfluous.

















