#Sustainability
Merino wool does not release microplastics into oceans, new study finds
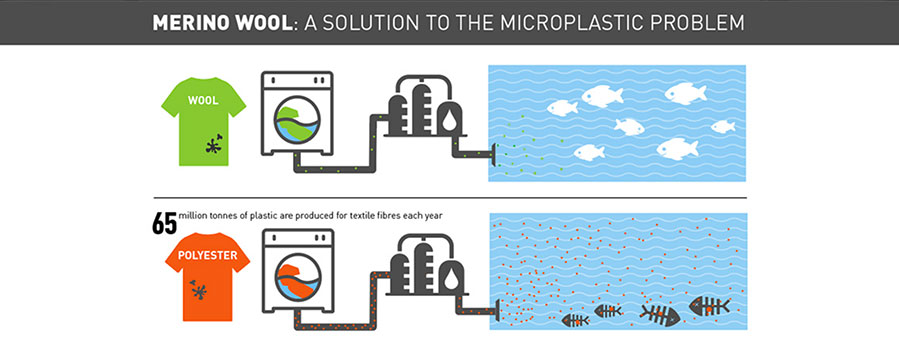
The scientific study - titled Microfibre Pollution and the Marine Biodegradation of Wool - has found that both untreated and machine washable wool readily biodegrade in marine environments, while synthetic fibres do not. The study also found the machine washable wool actually biodegrades at a faster rate than untreated wool fabrics and there was no evidence the treated wool’s polyamide resin coating added to microplastic pollution.
Previous estimates suggest as much as 20 per cent to 35 per cent of all primary source microplastics in the marine environment are from the use of synthetic clothing and a single polyester fleece garment can produce more than 1900 microfibres per wash.
In this latest study researchers compared the biodegradability of the two types of Merino wool in sea water to the biodegradability of viscose rayon, polyester, nylon and polypropylene. Residues were examined using scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. All fabrics were washed repeatedly before testing to simulate a partial garment lifetime. The rate of biodegradation was then compared to that of a substance known to biodegrade readily, kraft paper pulp.
Scientists found untreated wool biodegraded at 20.3 per cent the rate of the pulp and the machine-washable wool biodegraded more than three times as quickly, at a rate of 67.3 per cent – the fastest of all fabrics.
At the tail-end was Nylon, biodegrading at a rate of just 0.8 percent, followed by polypropylene and polyester.
“Our research into wool and microplastics began back in 2016 when we investigated the current state of knowledge concerning microplastic pollution, focussing on microfibres from textiles,” explains The Woolmark Company Managing Director Stuart McCullough. “This initial body of research began the process of improving methodological development to account for microfibre release during the use phase in the Lifecycle Assessment of clothing.
“This latest scientific study is a significant addition to the body of research investigating the damage certain textiles cause to our environment. Wool has long been heralded the original eco fibre, but concerns had been raised about the machine-washable finish applied to wool and whether it added to the microplastic problem, so we wanted to clarify that issue. During these ever-changing troubled times it’s important to consider how well-intentioned consumers can make purchasing decisions that help look after the health of the environment. Choosing natural fibres, such as Merino wool is an important place to start.”












