#Research & Development
Tapes made from recycled carbon fibers for lightweight construction
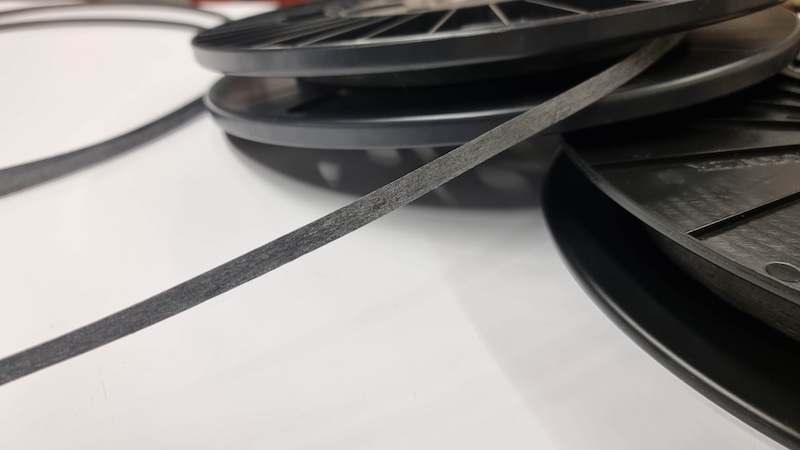

The German Institutes of Textile and Fiber Research Denkendorf (DITF) have developed highly oriented tapes made from recycled carbon fibers (rCF) suitable for reuse in high-performance applications such as structural components in the automotive sector.
Carbon fibers are usually produced from petroleum-based raw materials in an energy-intensive process that emits large amounts of CO2. The material has a global warming potential of around 20 - 65 kilograms of CO2 equivalents per kilogram. Nevertheless, the production of CFRP continues to increase and with it the amount of CFRP waste. This is because, depending on the processing method, up to 50 percent offcuts are generated during production. In addition, there are large quantities of CFRP waste in the form of components that have reached the end of their service life. In Europe alone, around 8,000 passenger aircrafts with cosiderable CFRP content are expected to be taken out of service by 2030.
Currently, only 15 percent of CFRP waste is recycled. The remaining 85 percent of these CFRP components end up in waste incineration plants or landfills at the end of their service life. Incineration can generate energy in the form of heat or electricity. However, recycling carbon fibers would contribute far more to climate and resource protection.
In recent years, various recycling processes for CFRP, such as pyrolysis or solvolysis, have therefore been further developed in order to recover high-quality carbon fibers.
Compared to virgin fibers, the possible uses of recycled carbon fibers are significantly limited. In a virgin fiber product, carbon fibers are usually present in filament strands of technically unlimited length and oriented in the direction of the load. In this way, the carbon fiber unfolds its full potential, as it has its maximum strength in the fiber direction. Recycling inevitably results in a shortening of the carbon fibers to lengths in the micrometer to centimeter range. In addition, the orientation of the carbon fibers is lost and the fibers are initially in a tangled position.
The DITF have been successfully working for around 15 years on adapting classic spinning processes to the new fiber material rCF. The aim is to develop a new category of rCF semi-finished products and improve their mechanical properties so that they can actually replace virgin fiber material in structural applications. Only then will carbon fiber-based composite materials be truly recyclable.
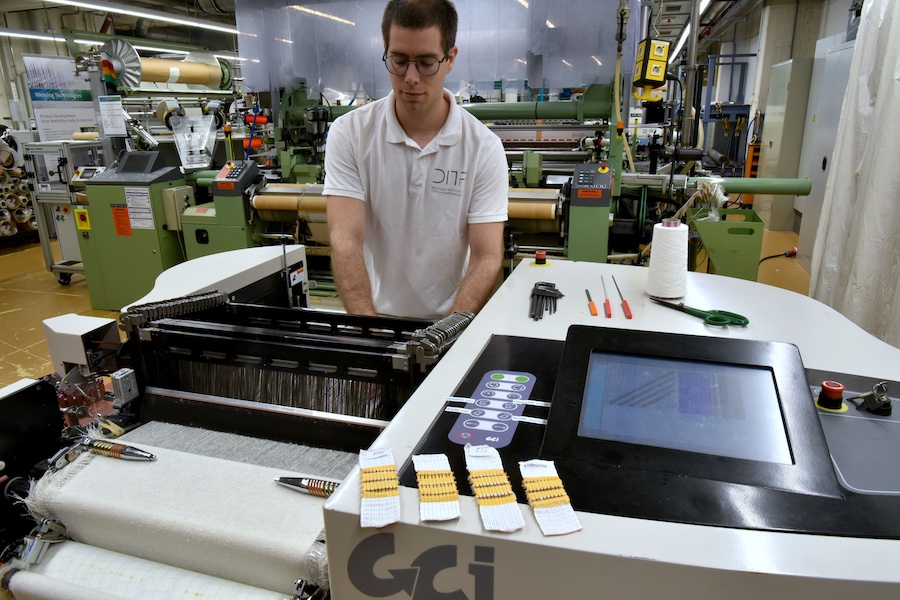
In order to produce an oriented semi-finished product similar to a carbon product from virgin fibers, it is crucial to eliminate the tangled position of the rCF and to align the fibers parallel to each other. One promising way of achieving this is the production of highly oriented tapes.
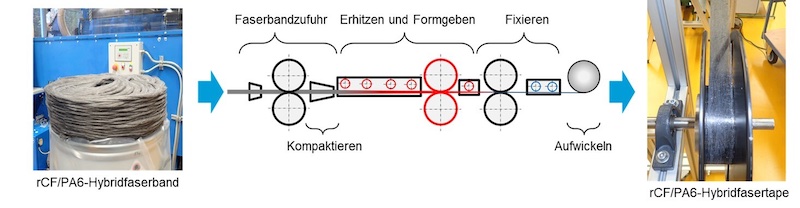
In a first step, the carbon fibers are opened and mixed with thermoplastic matrix fibers (polyamide 6). The fiber mixture is then further separated and oriented in a carding process modified for the processing of carbon fibers. At the outlet of the carding machine, the fiber card web produced in the carding process is combined into a fiber sliver and deposited in a can. This rCF/PA6 fiber sliver is the starting material for the subsequent tape forming process and already has a pre-orientation of the carbon fibers. The orientation of the fibers can be increased in the subsequent drawing process. By drawing the fiber tape, the fibers are moved in the direction of draft and aligned longitudinally. The final process step is tape formation, in which the fiber tape is under tension formed into the desired shape and then fixed into a continuous tape structure. During fixation, the thermoplastic fibers melt partially or completely and then solidify.
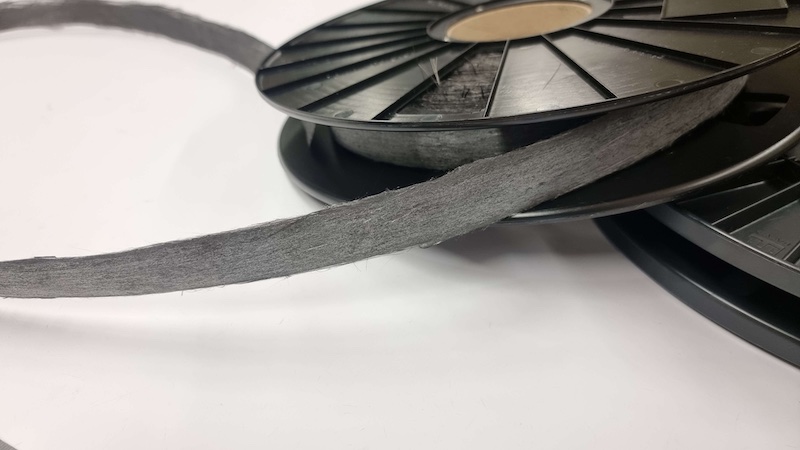

This technology developed at the DITF for the production of highly oriented rCF tapes was used as part of the “Infinity” research project (03LB3006) to demonstrate a sustainable and fiber-friendly recycling cycle for CFRP. Based on the “Infinity” tapes, a composite material was developed that achieved 88 percent of the tensile strength and tensile modulus of a comparable virgin fiber product. In addition, a life cycle analysis showed that the global warming potential is reduced by approx. 49 percent when using pyrolysis fibers and by approx. 66 percent for rCF from production waste.
The findings thus illustrate a way towards true substitution of virgin fiber CFRP with recycled CFRP instead of downcycling to low-orientation materials and the associated loss of mechanical properties.