#Recycling / Circular Economy
Cutting material consumption by one-third is key to tackling climate change: study
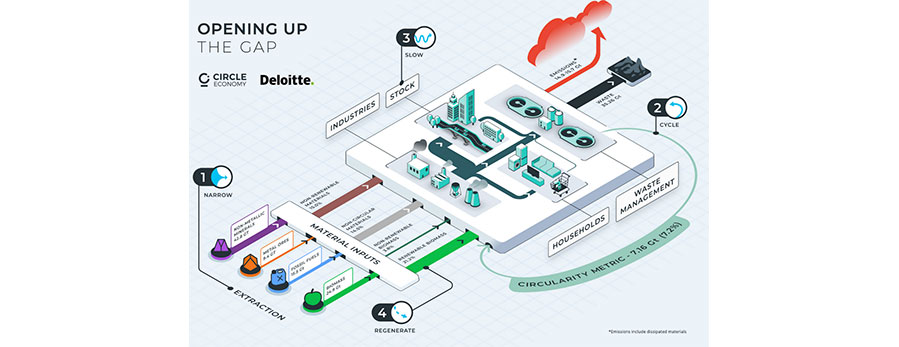
Reducing global material use through circular solutions, such as reuse, repair, and recycling of items, can limit global warming to 2-degrees and bring human activities back within safe planetary boundaries1, according to a new report by impact organisation Circle Economy, in collaboration with Deloitte. The report was launched today in Davos, at the World Economic Forum.
The global economy is measured to be 7.2% circular today—dropping from 9.1% in 2018 when Circle Economy first calculated the figure.2 It means that of the landmark 100 billion tonnes of virgin materials extracted from Earth annually, only 7.2% make it back into the economy in the form of recycled materials. Over the past six years alone, the global economy has extracted and used almost as many materials as over the course of the entire 20th century, finds the Circularity Gap Report 2023.
Matthew Fraser, Head of Research and Development at Circle Economy, said that this low level of circularity ‘demonstrates how reliant the global economy is on new, virgin materials. There is huge potential to increase the global economy’s use of secondary materials.’
Current linear processes don’t just sap the planet’s finite materials—they also produce tonnes of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and waste, a considerable part of which can be prevented. According to the study, key societal needs—such as nutrition and housing—could be fulfilled with just 70% of the materials the world economy currently consumes. Crucially, cutting material extraction by 30% will hugely improve environmental health across land, sea and air. The key to this reduction lies in the transition from fossil fuels to more renewable energy sources and lowering demand for high-volume minerals, such as sand and gravel, which are largely used for housing and infrastructure. In practice, it means boosting renewable energy and renovating old buildings and infrastructure instead of constructing new ones, in combination with other measures. The most appropriate approaches will vary significantly between geographies given the just transition imperative acknowledged in the 2015 Paris Agreement.
The potential reduction of material use will look different across global regions, some like the USA and EU member states, must radically reduce their material extraction and use, as they currently consume 31% of materials. While others such as China will need to stabilise their material consumption.
‘The linear economy has a number of detrimental effects on the environment that significantly affect peoples' wellbeing. Our research shows that by adopting circular economy practices, we can cut material extraction, continue to prosper, and return to living within the safe limits of this planet,’ points out Martijn Lopes Cardozo, CEO at Circle Economy.
Delivering more benefit with fewer materials
According to the Circularity Gap Report 2023, four key global systems account for the lion’s share of global emissions and waste—the Built environment, Food systems, Mobility and transport, and Manufactured goods and consumables. 16 ambitious circular economy solutions implemented across these systems can reverse the current overshoot of five planetary boundaries, ensuring safety for land, air and water and limiting global warming to below 2-degrees.
The food system now occupies roughly half of the habitable surface of the planet. It is responsible for one-third of global GHG emissions, 8–10% of which relate to the production of lost and wasted food. Transitioning to a circular food system would include cutting food waste by improving transport and storage management, supporting healthy soils to keep land arable for longer and focusing on local, seasonal and organic produce to reduce the need for toxic fertilisers, fuel and transportation.
The built environment accounts for roughly 40% of global GHG emissions, with cement production alone contributing around 7% of the CO2 released into the atmosphere globally. Boosting building’s energy efficiency and repurposing existing building stock are just some of the ways this could be improved.
The mobility and transport system is a major driver of climate change and ocean acidification, responsible for approximately 25% of GHG emissions globally. In a circular mobility system, walking, cycling and remote work would be key, as would investment in high-quality public transport and a transition to electric vehicles.
Manufactured goods and consumables imply highly energy- and material-intensive industrial processes. The Circularity Gap Report 2023 estimates that over one-quarter of global solid waste generation is industrial waste. This could be improved with more sustainable fashion practices, promotion of responsible buying and extending the lifetime of machinery.
Dieuwertje Ewalts, director Circular economy and sustainability at Deloitte, commented: ‘These findings reinforce that we have reached a point where the planet cannot keep up with the human demand for material goods. Circularity offers us the opportunity to reduce planetary pressures. Involvement from business and the creation of more circular products going forward will be key in creating a positive impact for both the planet and society.’
1) Nine quantifiable and interrelated planetary boundaries within which humanity can safely continue to thrive: crossing these boundaries increases the risk of causing irreversible environmental changes, threatening human life on Earth. Developed in 2009 by Johan Rockström, former director of the Stockholm Resilience Centre at Stockholm University, together with 28 world renowned scientists. Find out more on the Stockholm Resilience Centre website.
2) Circle Economy has improved its methodology each year, with 2023 marking the most significant modification to our calculations. While this allows us to make more accurate accounts, it also means that this year’s Circularity Metric can’t be directly or accurately compared with previous years. Nevertheless, we can say with certainty that the rising rate of global material extraction and use is causing the rate of circularity to shrink.
















